MH Daily Bulletin: August 26
News relevant to the plastics industry:
At M. Holland
- M. Holland’s latest logistics outlook examines current challenges and industry trends that are impacting shipping, trucking and rail. Although the plastics industry is faring a little better than earlier this year, M. Holland’s experts predict disruption to continue well into 2023. Click here to read the full outlook for the remainder of 2022.
- M. Holland will be attending the North American Detroit Auto Show on Sept. 14-15. This annual showcase for emerging automotive technologies will be held at Huntington Place in Detroit, Michigan. If you’re attending, please RSVP for M. Holland’s reception or contact Mike Gumbko, Strategic Account Manager, to set up a meeting with our Automotive team.
- Market Expertise: M. Holland offers a host of resources to clients, prospects and suppliers across nine strategic markets.
Supply
- Oil prices slumped about 2% Thursday on worries that rising U.S. interest rates will weaken fuel demand. After surging the first five months of the year, crude has been in retreat, with losses deepening in the summer trading months.
- In mid-morning trading today, WTI futures were down 0.9% at $91.66/bbl, Brent was down 0.5% at $98.84/bbl, and U.S. natural gas was up 1.1% at $9.48/MMBtu.
- Texas is preparing to block banks and other financial firms from doing business in the state over their perceived lack of support for fossil fuels, the state comptroller said Thursday.
- OPEC’s president became the latest to back Saudi Arabia’s suggestion that the alliance cut output to reverse a recent decline in oil prices. The group’s exports rose 200,000 bpd in August, led by a boost in Iranian production.
- Global oil and gas exploration firms could generate combined cash flows of a record $1.4 trillion this year, according to Deloitte.
- Coal-fired power generation in the U.S. surged 16% in 2021 after falling for 10 years but is predicted to fall again as more plants switch to natural gas capacity:
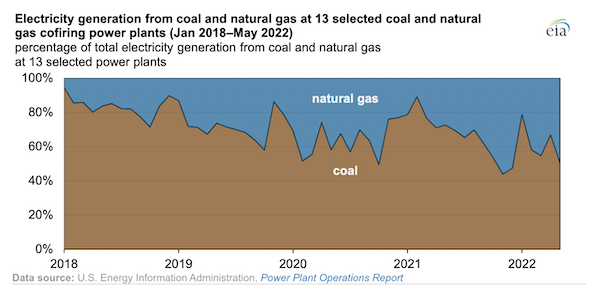
- More oil news related to the war in Europe:
- High energy prices are prompting radical changes by European governments and consumers, which could make energy rationing this winter less likely.
- Ash pits in a nearby coal facility disconnected Ukraine’s Zaporizhzhia nuclear plant from the nation’s power grid for the first time ever on Thursday. Ukrainian officials say reactor staff remedied the issue within hours, but fears remain over a possible mishap at Europe’s largest nuclear site that is now under Russia’s control.
- South Korea signed a $2.2 billion deal with Russia’s state-owned Rosatom to provide buildings and components for a new Egyptian nuclear plant.
- Spain will soon impose limits on building temperatures and lighting to curb the spiraling cost of energy.
- British energy executives say the country could see mass civil unrest if surging energy costs leave households unable to pay heating and electricity bills this winter. Officials raised a price cap on energy fees Thursday that could end up tripling monthly bills.
- Kosovo, a Balkan nation in Southeast Europe, is the continent’s first to see rolling blackouts amid rising energy shortages.
- China’s oil imports from Russia surged more than 50% from April to May, according to analyst firm Bimco.
- EU officials say they will urge the world’s biggest economies to improve their climate-change targets ahead of this year’s United Nations summit in November.
- Indian Oil Corp., the nation’s top refiner, plans to invest over $25 billion to achieve net-zero operational emissions by 2046.
- Australia will need to boost renewable generation fortyfold to achieve its net-zero emissions goal by 2050, analysts say.
Supply Chain
- Texans have paid over $1 billion in extra power fees this year as the state’s grid operator takes more measures, including keeping larger reserves, to avoid blackouts during record demand this summer.
- China’s Yangtze River basin has seen 70 straight days of extreme temperature and low rainfall, threatening the region that produces a third of the nation’s crops.
- The U.S.’s worst drought in a decade is sharply reducing corn harvests in major producing states including South Dakota, Iowa, Nebraska and Illinois.
- Water levels on rivers across the globe are receding due to widespread drought, posing serious risks to shipping routes, agriculture, energy supplies and drinking water.
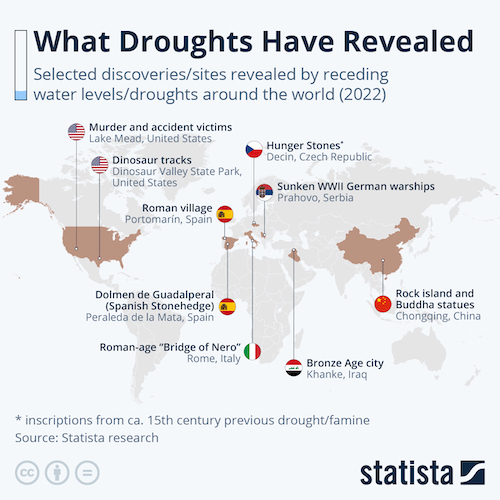
- Truck protests and other snarls led to a sharp drop in throughput at the Port of Oakland in July, with loaded container volumes falling 28% compared with a year ago.
- Maersk is dropping plans for China International Marine Containers to take over its refrigerated container-making unit after U.S. regulators questioned the $1 billion deal over antitrust grounds, saying it would have consolidated control of 90% of the world’s supply of cold-storage boxes.
- Earnings for very large crude carriers (VLCCs) have been climbing since June on strong growth in vessel demand. Tonnage rates rose by $65,000 per day from early June to mid-August, new data shows.
- Ship scrapping volumes are at historically low levels, with zero container ships sold into the recycling market so far this year, an industry first.
- Tennessee-based and privately owned Colonial Freight Systems is closing its doors after nearly 80 years in business.
- Kohl’s says it is canceling orders and marking down prices to clear excess inventory in the latter half of 2022.
- The U.S. president signed an order to release over $52 billion in domestic computer chip production subsidies.
- European brewer Carlsberg could soon be forced to halt production in Poland due to a shortage of CO2, as CO2 suppliers are unable to keep up with surging energy costs.
- Norway’s Yara, one of the world’s largest fertilizer makers, will join the growing list of ammonia suppliers in cutting production due to surging gas prices in Europe.
- French beauty company Coty says the “lipstick effect” — where high-income consumers buy more small products due to surging inflation — led to a 10% quarterly revenue surge, topping expectations.
- In the latest news from the auto industry:
- California regulators approved a trailblazing new plan to restrict and ultimately ban sales of gas-powered cars by 2035 in the U.S.’s largest auto market.
- Panasonic, a key Tesla supplier, is in talks to build an additional $4 billion electric vehicle battery plant in Oklahoma, coming on the heels of a similar investment announced for Kansas last month.
- Mercedes-Benz launched production of its first electric vehicle (EV) model at a massive plant in Alabama, which could produce up to 100,000 EVs next year, the automaker said.
- Lithium’s growing importance to the automotive industry is garnering increasing scrutiny from environmental concerns about mining it.
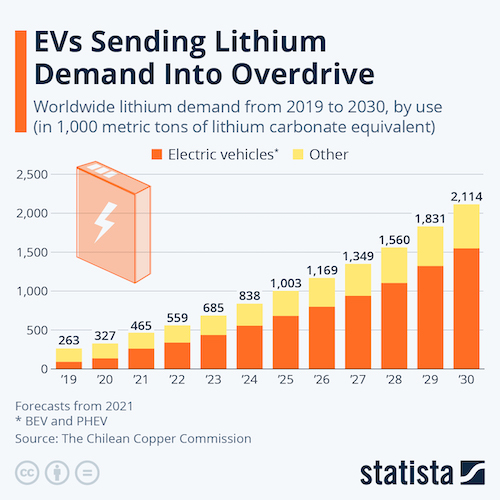
- Honda plans to slash production by up to 40% in Japan early next month amid persistent supply chain issues.
- Stellantis is halting some production in France through the weekend due to semiconductor shortages.
- Amazon signed a hydrogen supply deal with New York-based Plug Power Inc. with the aim of fueling tens of thousands of logistics machinery and trucks by 2025.
- China’s CATL is starting a service allowing drivers to rent and swap out batteries under a subscription model.
- GM’s electric vehicle (EV) sales were steadily ramping up from 2017 before exploding in 2020 and 2021, new data shows. The automaker is now fourth in global EV sales:
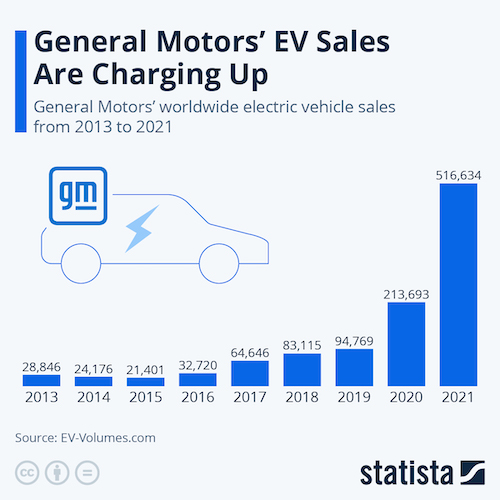
Domestic Markets
- The U.S. reported 90,675 new COVID-19 infections and 389 virus fatalities Thursday.
- Almost 40% of COVID-19 hospitalizations this spring were of vaccinated and boosted people, highlighting the success of Omicron subvariants in evading immunity.
- COVID-19 hospitalization rates in children under age 4 are up fivefold since the spring, according to the CDC.
- Fewer than 2% of infants and toddlers in New York City are fully vaccinated against COVID-19, as demand levels remain exceptionally low.
- Pfizer’s COVID-19 antiviral pill appears to provide little or no benefit to young adults but is effective in reducing the risk of hospitalization and death in older populations, according to new research.
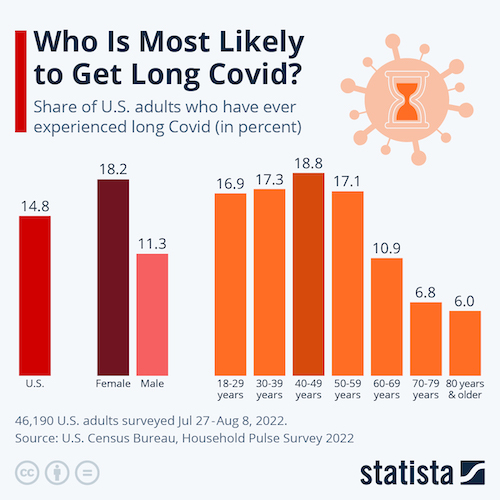
- Long-COVID is costing Americans an estimated $170 billion annually in lost wages, according to the Brookings Institution.
- A Florida county started the fall school year with a shortage of over 600 teachers, up threefold from last year, emblematic of the U.S.’s widespread teacher shortage brought on by pandemic pressures.
- U.S. Federal Reserve officials are wavering between a 50-basis-point and a 75-basis-point interest-rate hike at next month’s meeting of the central bank, according to comments made Thursday. Some have indicated the U.S. benchmark rate should hit at least 3.75% by year’s end.
- U.S. corporate profit margins — as measured by after-tax profits as a share of gross value added — improved in the second quarter to 15.5%, the highest level since 1950, as firms managed to pass on rising costs to consumers.
- The number of 18- to 24-year-olds out of the labor market rose by 118,000 from a year ago to 447,000 in the second quarter, the highest level of the pandemic.
- The average U.S. mortgage rate climbed to 5.5% this week, nearly double the same time last year, according to Freddie Mac.
- Home Partners of America, the single-family landlord owned by Blackstone Inc., plans to stop buying homes in 38 U.S. cities, becoming the latest institutional investor to back away from an overheated housing market.
- The average U.S. new-vehicle loan hit a record-high $40,290 in the second quarter, according to Experian. Meanwhile, more people are financing used-car purchases compared to a year ago.
- In the latest news from second-quarter earnings season:
- Dell reported its slowest quarterly revenue growth in 1.5 years after taking hits from a surge in the U.S. dollar and COVID-19 flare-ups in China, its second-largest market. The firm joined rivals in predicting slumping PC sales this year following a two-year pandemic boom.
- Peloton posted a $1.2 billion quarterly loss after revenue fell 30% due to plunging demand for its high-end bikes and treadmills.
- Dollar Tree trimmed its full-year profit forecast as it struggles to compete with other retailers, including Walmart and Target, that are offering major discounts to get rid of excess inventories.
- Dollar General slightly raised its 2022 sales forecast after gross margins improved in the latest quarter on higher consumer demand.
- Abercrombie & Fitch cut its full-year forecasts after reporting a surprise quarterly loss and a sharp decline in sales for its key Hollister brand.
- Gap Inc. withdrew its full-year outlook after suffering an 8% revenue decline in the second quarter.
International Markets
- Global COVID-19 fatalities this year surpassed 1 million Thursday, according to the WHO. Nearly 6.5 million people have died since the start of the pandemic.
- China eased COVID-19 reporting requirements for cross-border travelers Thursday, marking one of its first policy relaxations in months.
- A recent spike in COVID-19 infections has prompted Hong Kong to renew testing and limited restrictions.
- British construction activity dipped 1.4% in June in the sharpest decline so far this year, according to building suppliers.
- German business sentiment in August fell to its lowest reading in two years amid high uncertainty caused by Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, according to the widely tracked Ifo institute’s survey.
- Beijing announced over $1 trillion of government funding for construction projects in recent months, potentially giving a boost to the nation’s flagging economy, economists say.
- Toronto-Dominion Bank, Canada’s second-largest lender, posted better-than-expected quarterly results Thursday but warned that the U.S. and Canada will see slower economic growth in 2022 due to higher interest rates.
- Norwegian Air saw net profit rise to $129.5 billion in the second quarter on rebounding travel demand but said surging energy costs will dent its earnings for the full year.
- Sony is raising the price of its PlayStation 5 console by as much as 20% in some markets to reflect rising costs, the firm said.
- Global spending on technology, which includes cloud services, is expected to rise about 3% this year, well below the 10% annual growth rate of 2021 and the 7% gain from 2020, according to research firm Gartner.
Some sources linked are subscription services.