COVID-19 Bulletin: February 28
More news relevant to the plastics industry:
Some sources linked are subscription services.
Supply
- Oil prices fell over 1% to pre-invasion levels Friday after several days of volatile trading. For the full week, Brent rose about 4.7%, while WTI rose about 0.6%.
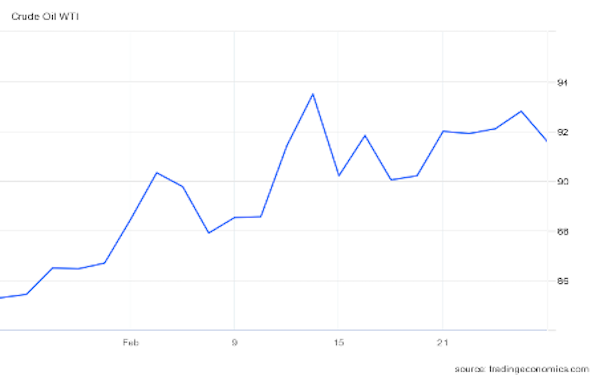
- In mid-morning trading today, Brent futures were up 2.7% at $100.61/bbl, WTI was up 3.6% at $94.92/bbl, and U.S. natural gas was 0.2% higher at $4.48/MMBtu.
- War in Eastern Europe continues to ripple through global oil markets:
- BP said it would exit its nearly 20% stake in Russia’s state-controlled oil producer Rosneft, a momentous move that could lose the British major $25 billion and a third of its oil and gas production.
- Oil-rich Norway’s sovereign wealth fund, the world’s largest, announced plans to divest from all its investments in Russia.
- Tanker rates rose sharply last week on combined effects of a “war risk” premium, Russian supply volatility and higher fuel costs. Some traders reported a $13,971 leap for medium-sized Aframax tankers on Friday, while rates to load Russian crude are almost three times higher than pre-invasion levels.
- Top buyers of Russian oil are struggling to secure credit lines at Western banks or find ships to take crude away, pushing prices for Russia’s Urals crude cargoes to their lowest level in the post-Soviet period.
- The same countries sanctioning Russia continue to import large portions of their energy from the nation every day, complicating efforts to effectively punish the nation. Sanctions have largely been targeted to avoid the energy sector so far.
- Asia’s coal benchmark surged to a four-month high Friday.
- Russia’s invasion of Ukraine could force the breakup of the OPEC+ alliance.
- OPEC+ will likely stick to a modest 400,000-bpd output increase for April when the group convenes this Wednesday, delegates say, despite the risk of oil prices surging past $100/bbl.
- Boosting production at the Netherlands’ massive Groningen gas field is a last resort to help energy-starved Europe, officials say, as concerns over triggering earthquakes outweigh surging demand.
- Germany will support two new LNG terminals in a bid to quickly reduce reliance on Russian gas.
- Europe’s energy bill could surge to a record-high $1.2 trillion this year, almost four times the level of 2021, Citigroup estimates.
- Louisiana’s newest LNG export terminal is ready to release its first loaded tanker for export to Europe, a well-timed move as Europe loses supplies from Russia.
- New data shows that China has been loading up its reserves with new oil purchases despite agreeing last November to begin releasing reserves to help cool the global market.
- Average U.S. diesel prices are up 44 cents per gallon this year, while the national average price of $4.055/gallon last week was the highest in nine years.
- Active U.S. oil and gas rigs rose by five to 650 last week, the 18th consecutive weekly rise and 248 rigs more than the same time last year, Baker Hughes said.
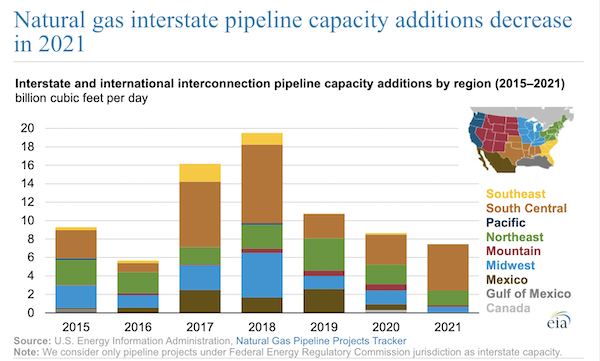
- The U.S. added just 7.44 billion cubic feet per day of interstate natural gas pipeline capacity in 2021, a six-year low, with more than two-thirds of the increase in Texas and Gulf Coast markets:
- Last week’s auction of offshore wind rights between Long Island and New Jersey fetched a record $4.37 billion, over three times the revenue from all U.S. oil and gas lease sales over the past five years.
- Union workers locked out of their jobs at a Texas oil refinery for nearly 10 months have agreed to a contract with Exxon Mobil and are set to resume work in early March.
- Mexico’s trade deficit widened fivefold in January from a year earlier on a 55% rise in oil imports, as state refiners struggle to meet the administration’s goal of oil self-sufficiency.
Supply Chain
- War in Eastern Europe continues to ripple through supply chains:
- China is restricting financing for Russian commodities in an apparent attempt to comply with U.S. and European sanctions.
- Flying cargo between Europe and Asia will become more expensive after Europe closed its airspace to Russia and Russia responded in kind, likely making some routes unviable. For example, Virgin Atlantic cancelled all cargo flights between London and Shanghai.
- Commercial airlines are avoiding airspace around Ukraine, Moldova and Belarus.
- UPS and FedEx are halting all delivery services to Russia and Ukraine.
- Greece told all Greek ships to immediately leave Ukrainian and Russian waters in the Black Sea, possibly lowering rates in regions where the ships move.
- The U.K. is considering a move to ban all Russian ships from its ports.
- Renault is suspending production at its Russian plants this week, while Volkswagen idled two German factories due to shortages from Ukrainian suppliers. Analysts predict automakers will lose about 400,000 vehicle sales to the conflict.
- Daimler Truck is suspending its business activities in Russia following the nation’s invasion of Ukraine.
- The U.S., Japan and Taiwan each announced sanctions aimed at punishing Russia by restricting sales of semiconductors and other cutting-edge technologies.
- The Baltic Exchange Dry Index, a benchmark for the price of moving major raw materials by sea, fell 1.7% to 2,040 Monday amid lower rates for the largest and second-largest vessels.
- Combined exports from the ports of Seattle and Tacoma fell 36% in January to the lowest level in records dating to 2015, as more vessels skipped calls to avoid congestion.
- The vacancy rate for warehouse space in the U.S. remained under 4% for the entirety of 2021, an industry first.
- American Airlines is cutting more flights from its summer schedule due to delays in Boeing’s 787 deliveries.
- Deere raised 2022 income forecasts despite a 26% decrease in profit last quarter, saying strong demand for farm and construction machinery will outweigh higher production costs.
- General Electric warned that supply chain problems, labor shortages and inflation would weigh on first-half financial results this year.
- The U.S. Justice Department is working with other countries to identify and prosecute companies that illegally exploit supply chain disruptions for profit.
- The White House is set to unveil tighter nitrogen oxide emissions standards on heavy-duty trucks in the coming weeks, a move facing criticism over the potential to worsen supply chain congestion.
- Ford is halting production at its Kansas City F-150 plant this week due to computer chip shortages.
- Walmart is doubling down on e-commerce fulfillment and delivery, aiming to build scores of automated centers attached to stores and expand its network to provide rapid-delivery services.
- Icelandic container line Eimskip projects continued high earnings this year after seeing profit jump nearly 10-fold to $45 million in 2021.
Domestic Markets
- The U.S. reported 7,464 new COVID-19 infections and 182 virus fatalities Sunday. Although daily case counts are down over 90% from their January peak, the streak of daily fatalities above 2,000 continues and has now extended more than twice as long as the 2,000+ daily death streak of last fall’s Delta wave.
- Over 70% of Americans can now stop wearing masks and no longer need to social distance or avoid crowded indoor spaces, according to the CDC’s revised pandemic guidelines.
- New York state will lift its indoor school mask mandate March 2, while New York City’s COVID-19 vaccine mandate for bars and restaurants will end March 7.
- California dropped most of its remaining pandemic measures but retained an emergency status that allows state testing and vaccination programs to continue along with expanded tele-health services.
- Illinois dropped its statewide mask mandate for public school students, although some cities, including Chicago, are choosing to keep their own.
- Nearly half of the 500 million free COVID-19 tests recently made available by the White House have not been claimed as cases plummet across the nation. Booster-shot rates are also down, with just half of eligible Americans having received one.
- The U.S.’s disability information hotline is being expanded to help people with ordering COVID-19 tests.
- More states are deploying National Guard troops to make up for staff shortages in public schools.
- U.S. core inflation rose 5.2% in January from a year ago, the sharpest 12-month increase in almost 40 years.
- Personal spending in the U.S. jumped a surprisingly high 2.1% month over month in January, the biggest increase since March of last year in a sign that consumption remained robust despite high inflation and COVID-19 infections. Meanwhile, savings rates have dipped to pre-pandemic levels.
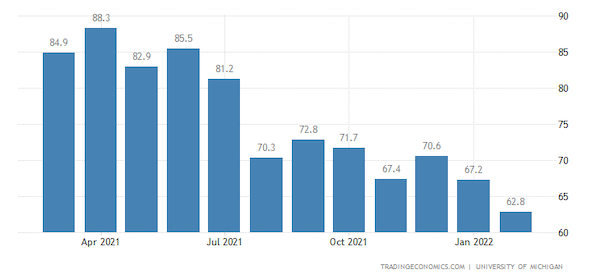
- A measure of U.S. consumer sentiment was revised upward for February, while remaining at the lowest level of the past decade, the University of Michigan said.
- New orders for U.S.-made durable goods rose 1.6% month over month in January, the fourth straight month of increases and nearly double market expectations.
- Over half of U.S. firms surveyed by the Kansas City Federal Reserve have passed less than 40% of inflationary costs to consumers due to how quickly labor and material costs are rising.
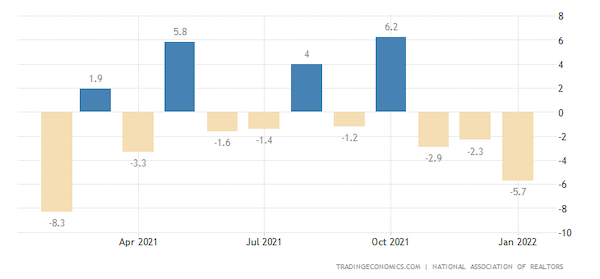
- The number of signed contracts to buy existing U.S. homes plunged 5.7% in January from a month earlier, the sharpest drop in almost a year.
- January’s 1.5% gain in used-car prices was wiped out during the first two weeks of February, although prices are still up almost 40% on a yearly basis.
- GM is banking on fee-based software services — such as a program that predicts vehicle maintenance — to boost revenue in the years ahead.
- California is the first state to surpass 1 million total electric vehicle sales, more than the next 10 states combined.
- Amazon-backed electric vehicle (EV) startup Rivian is slowly ramping up production and hopes to have a 10% share of the EV market by 2030, executives said.
International Markets
- The economic fallout of war in Eastern Europe is spreading:
- New U.S. and European sanctions on Russia will freeze roughly half the nation’s foreign-currency reserves and sever some Russian banks from the SWIFT global payment system, curtailing the nation’s ability to import and export goods.
- Russia’s central bank more than doubled its key interest rate to 20% to stem the collapse of the ruble, which fell to a record low this morning, worth less than one U.S. penny.
- Early estimates suggest Russia’s GDP growth could fall two percentage points this year due to sanctions.
- A growing number of countries — including the entirety of the EU — are closing their airspace to Russian planes in response to Russia’s invasion of Ukraine, disrupting international flight patterns. Russia has retaliated with its own flight bans in every instance.
- The disruption in Ukraine agriculture and planting schedules could add to global food inflation for months or years.
- The BA.2 subvariant of Omicron now accounts for 1 in every 5 new COVID-19 cases across the globe and is 30% more transmissible than its parent strain, the World Health Organization says.
- Hong Kong reported an 821% spike in new COVID-19 cases over the last two weeks, reporting over 26,000 new infections and 83 virus-related deaths Sunday, overwhelming hospitals and pushing its morgues to near capacity.
- South Korea posted a record 112 single-day COVID-19 fatalities over the weekend, as the nation’s worst ever virus wave intensifies.
- Retail sales in Australia were strong in January despite the continued threat of the Omicron variant, jumping 1.8% to $23.3 billion.
- Mexico’s economic activity was flat in the fourth quarter of 2021, narrowly avoiding recession territory, as a decline in services offset increases in industrial output and agricultural production.
- Germany’s producer prices skyrocketed 25% in January in the sharpest annual growth on record.
At M. Holland
- M. Holland’s 3D Printing group offers a rapid response alternative for producing selected parts where resin availability is tight. For more information, email our 3D Printing team.
- Market Expertise: M. Holland offers a host of resources to clients, prospects and suppliers across nine strategic markets.
For all COVID-19 updates and notices, please refer to the M. Holland website.